PGT-M
Right Embryo
A genetic test designed to reduce the risk of having
a child with an inherited condition


PGT-M
Right Embryo
A genetic test designed to reduce the risk of having
a child with an inherited condition

Fast-Track PGT-M Service: Empowering Families and Clinicians
Leveraging cutting-edge amplification technology to provide a new premium Fast-Track PGT-M service.
What to Expect
 Previous testing process
Previous testing process
2-3 months
 NEW Fast-Track PGT-M
NEW Fast-Track PGT-M
4 weeks*
Benefits of Fast-Track PGT-M service
 Potentially improving patient experience
Potentially improving patient experience
 Could facilitate earlier IVF cycling (following case review and acceptance)
Could facilitate earlier IVF cycling (following case review and acceptance)
 Designed to streamline the PGT-M process for clinics and patients
Designed to streamline the PGT-M process for clinics and patients
A legacy of PGT innovation
CooperSurgical® boasts 30+ years of PGT-M experience, with over 10,000 procedures conducted.¹ Our technology carries on the tradition established by those pioneers who performed the first PGT-M cases,² and played an integral role in shaping our genomics organization.
Fast-Track PGT-M service
We’re excited to introduce a revolutionary amplification technology, unique to CooperSurgical, that will improve the patient experience while streamlining processes for the clinician.
* Effective form January 1st, 2024, all referred qualifying PGT-M cases will be subject to a 4-week turnaround that is initiated upon completion of case acceptance and receipt of required materials.
1. Internal CooperSurgical data
2. Handyside AH, Lesko JG, Tarín JJ, Winston RM, Hughes MR. Birth of a normal girl after in vitro fertilization and preimplantation diagnostic testing for cystic fibrosis. New England Journal of Medicine. 1992 Sep 24;327(13):905-9.
Common disorders** covered by Fast-Track PGT-M service
Most frequent disorders
Please contact CooperSurgical to confirm whether specific disorders can be accepted
Cystic Fibrosis
Spinal muscular atrophy (variations)
Fragile X syndrome
Sickle cell anemia
Hereditary breast-ovarian cancer 1
Hereditary breast and ovarian cancer syndrome (BRCA1/2)
Huntington Disease
Myotonic dystrophy 1+2
Neurofibromatosis 1+2
21-hydroxylase deficient congenital adrenal hyperplasia
Hemophilia A
Familial adenomatous polyposis
Marfan syndrome
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (PKD1/2)
**These are examples of common conditions that may be available for the Fast-Track service, however, CooperSurgical reserves the right to review cases based upon technical factors related to the specific mutation.
![]()
High accuracy – Improved genome coverage leads to better confidence in our results.
Choose CooperSurgical® Genomics Testing
All our innovation requires a significant investment of our resources and time. At CooperSurgical we believe that this cost should not be passed onto the patient, so the innovations and improvements to PGT-M described here, will not increase the cost to you or your patients. Furthermore, you can rest assured that you will receive the same quality of services you’ve come to expect.
Your Questions Answered
Q: Do I need to change any of my laboratory processes?
A: There are no required changes to your laboratory processes.
Q: Will there be an added cost for the Fast-Track PGT-M service?
A: No, there is no added cost for this service.
Q: Will there be any changes to the report?
A: No, there will not be any changes to the report format or delivery.
Q: When will I be able to benefit from this service?
A: Cases referred after January 1st, 2024, will benefit from this streamlined service.
For people who know they are at increased risk of passing on a specific genetic condition.
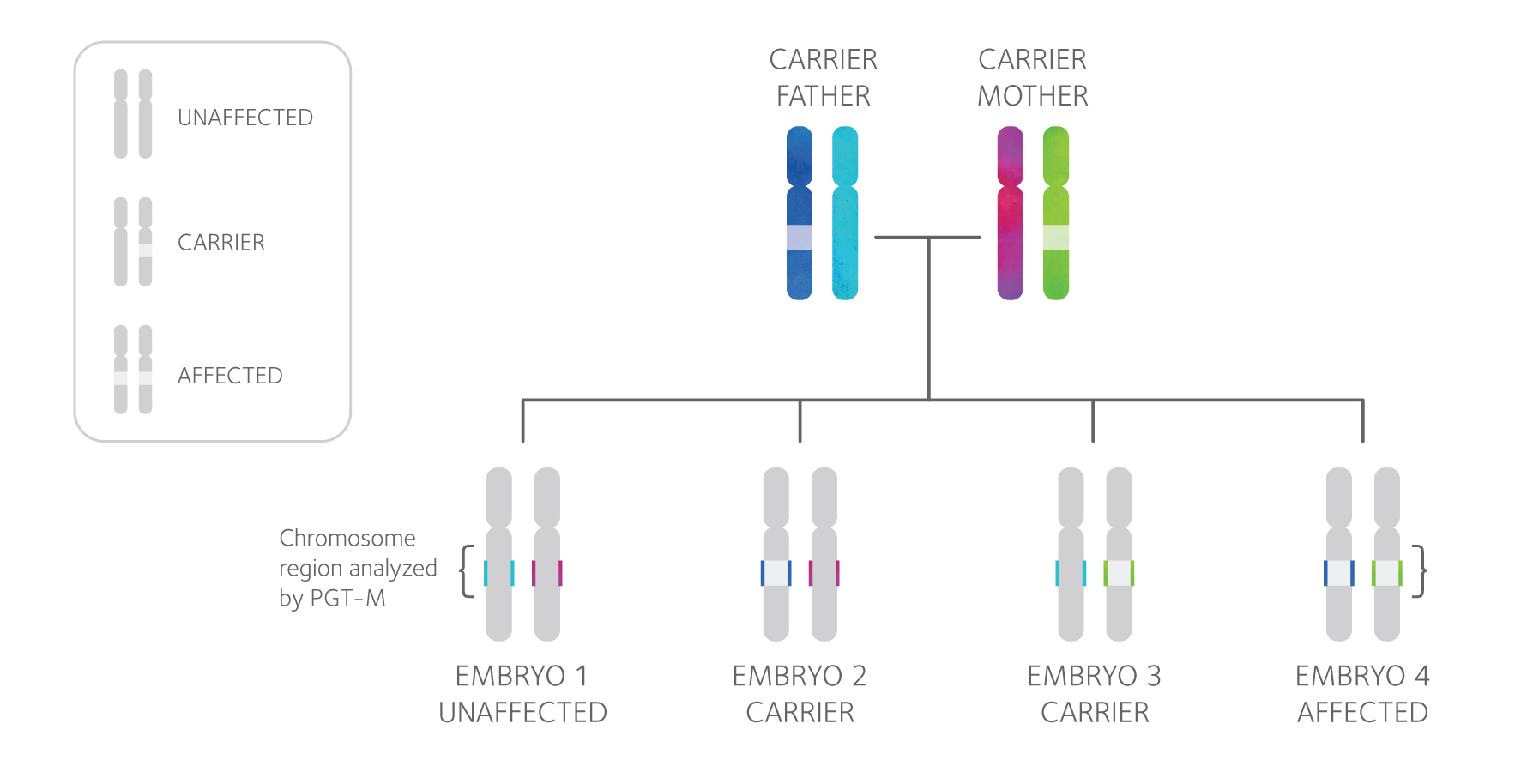
PGT-M, or preimplantation genetic testing for monogenic/single gene defects, can be performed prior to pregnancy to greatly reduce the risk of having an affected child.
PGT-M involves testing embryos created through in vitro fertilization (IVF) and then transferring unaffected embryos.
Key Product Information

Who is it for?
PGT-M is appropriate for people who are at high-risk of passing on a specific single gene disorder. You may consider PGT-M if:
- You and your partner are carriers of the same autosomal recessive condition (e.g. Cystic fibrosis)
- You are a carrier of an X-linked condition (e.g. Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy)
- You or your partner have an autosomal dominant condition (e.g. Huntington disease)
- You or your partner have a mutation associated with a hereditary cancer syndrome (e.g. BRCA1 & 2)
- You had a child or pregnancy with a single gene disorder
- You want to perform HLA matching
PGT-M Technology
PGT-M testing involves a close examination of both the mutation an individual carries and the area of the chromosome surrounding it, shown above as the colored segment of each chromosome. Each PGT-M test design is unique and specific to the family, so DNA samples from both partners, and often additional family members, will be requested in order to design a test. Then, linkage analysis is used to determine the “genetic fingerprint” of the mutation and diagnose each tested embryo as affected or unaffected.
The PGT-M/SR Experience
CooperSurgical is the pioneer and worldwide leader of PGT-M/SR. Our team performed the first-ever PGT-M procedure, and has since performed more PGT-M/SR cases than all other labs combined. This level of experience allows us to confidently accept even the most complex cases, which are often turned down by other labs.
![]()
The PGT-M Process

Case review
Ordering provider submits a TRF along with genetic testing reports for case review and approval.

Genetic consultation
Registered patients speak with a genetic counselor
(PGT-M: discuss if additional genetic testing of the couple or other family members is required).

PGT-M process
PGT lab collects DNA samples from the couple and appropriate family members and designs a test unique to each family.

IVF
In vitro fertilization is performed and the resulting embryos are incubated.

Embryo biopsy
An embryologist carefully removes a small cell sample from each embryo.

Vitrification
Embryos are frozen while awaiting PGT results.

PGT-M
Biopsied samples are sent to the PGT laboratory, testing is performed, and results are released to the IVF center.

Embryo transfer
If available, a chromosomally normal embryo is selected for transfer. Additional euploid embryos can remain frozen for future use.
Documents
Reproductive Genetic Testing Brochure – Czech
Reproductive Genetic Testing Brochure – Finnish
Reproductive Genetic Testing Brochure – French
Reproductive Genetic Testing Brochure – German
Reproductive Genetic Testing Brochure – Greek
Reproductive Genetic Testing Brochure – Italian
Reproductive Genetic Testing Brochure – Latvian
Reproductive Genetic Testing Brochure – Spanish(LATAM)
Reproductive Genetic Testing Brochure – Spanish
Reproductive Genetic Testing Brochure – Turkish
PGT-A Clinician Brochure – Czech
PGT-A Clinician Brochure – French
PGT-A Clinician Brochure – Greek
PGT-A Clinician Brochure – Italian
PGT-A Clinician Brochure – Portuguese
PGT-A Clinician Brochure – Spanish
PGT-A Clinician Brochure – Spanish LATAM
PGT-A Clinician Brochure – Thai
PGT-A Clinician Brochure – Turkish

 My Clinic is in the United States
My Clinic is in the United States My Clinic is in Canada
My Clinic is in Canada Previous testing process
Previous testing process